Molluscum contagiosum is a common skin infection that’s caused by a virus. It can spread easily and linger for months or even years.
What Are the Symptoms of Molluscum Contagiosum?
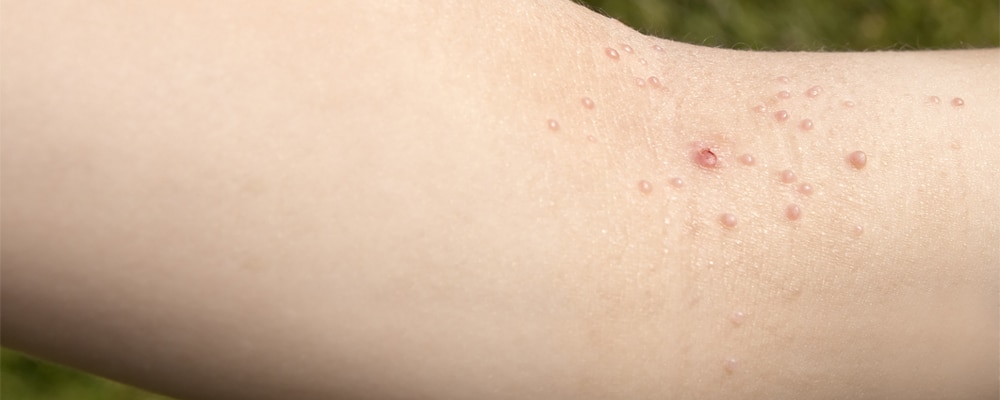
This skin disease causes pink, white or flesh-colored bumps with a dimple or pit in the center to form on your skin. They often look pearly and smooth and feel firm, and they usually range in size from as small as a pinhead to as large as a pencil eraser. They can form anywhere on the body but are most often found on the face, neck, armpits, arms, abdomen, tops of the hands, or on the genitals.
Bumps caused by molluscum contagiosum may turn red, itch or become sore or swollen. They can sometimes resolve on their own within 6 to 12 months but may take as long as 4 years. They usually don’t cause scarring.
Most people will get about 10 to 20 bumps, but if you have a weakened immune system, you may have many more.
When Should You See Your Doctor?
You should see your doctor as soon as you can when you notice the bumps. They can sometimes look at the bumps and tell you have molluscum contagiosum, but it may be necessary to take skin scrapings from your infected areas to view under a microscope. This helps eliminate other possible cause of bumps, such as warts or skin cancer.
Sometimes your bumps can be removed to keep them from spreading. You may receive an anesthetic beforehand to help relieve discomfort before your doctor scrapes, freezes (performs cryotherapy), uses a laser or uses cantharidin, a medicine that causes blisters that lift off the bumps.
If you have many bumps or large bumps, treatments may need to be repeated. You may also receive medicine to use at home, such as a retinoid or antiviral medication that’s applied to your bumps.
How Does Molluscum Contagiosum Spread?
Molluscum contagiosum spreads easily from person to person by direct contact or by touching an item that’s contaminated with the virus, such as a towel or mat. Although it often affects children, adults can also get molluscum contagiosum, especially if they have a weakened immune system.
How Can You Reduce Your Risk of Getting It?
The following steps can help reduce your risk of contracting or spreading molluscum contagiosum:
- Wash your hands: Keeping your hands clean can remove germs that you can pick up from other people or from surfaces that they’ve touched.
- Take precautions when playing sports: Don’t share towels, clothing or other personal items.
- Don’t touch your bumps: Touching or shaving over the affected area can spread the virus.
If you have bumps that could be symptoms of molluscum contagiosum, contact Skin Care Research or call us at 561-948-3116. Our research center has more than 25 years of experience with clinical trials that focus on a variety of skin conditions.